quantify_scheduler.visualization.circuit_diagram¶
Plotting functions used in the visualization backend of the sequencer.
Module Contents¶
Functions¶
|
A box for a single gate containing a label. |
|
Adds a visual indicator for a Baseband pulse to the mathplotlib.axes.Axis |
|
Adds a visual indicator for a Modulated pulse to the mathplotlib.axes.Axis |
|
A simple meter to depict a measurement. |
|
Variation of the meter to depict a acquisition. |
|
Same as acq_meter, but also displays text. |
|
Markers to denote a CNOT gate between two qubits. |
|
Markers to denote a CZ gate between two qubits. |
|
A broken line to denote qubit initialization. |
|
Returns the name of a qubit in a pulse address. |
Creates a circuit diagram visualization of a schedule using matplotlib. |
- gate_box(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
A box for a single gate containing a label.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- pulse_baseband(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Adds a visual indicator for a Baseband pulse to the mathplotlib.axes.Axis instance.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- pulse_modulated(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Adds a visual indicator for a Modulated pulse to the mathplotlib.axes.Axis instance.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- meter(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
A simple meter to depict a measurement.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- acq_meter(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Variation of the meter to depict a acquisition.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- acq_meter_text(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Same as acq_meter, but also displays text.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- cnot(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Markers to denote a CNOT gate between two qubits.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- cz(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
Markers to denote a CZ gate between two qubits.
- Parameters:
ax –
time –
qubit_idxs –
text –
- reset(ax: matplotlib.axes.Axes, time: float, qubit_idxs: List[int], text: str, **kw)[source]¶
A broken line to denote qubit initialization.
- Parameters:
ax – matplotlib axis object.
time – x position to draw the reset on
qubit_idxs – indices of the qubits that the reset is performed on.
text –
- _locate_qubit_in_address(qubit_map, address)[source]¶
Returns the name of a qubit in a pulse address.
- circuit_diagram_matplotlib(schedule: quantify_scheduler.Schedule, figsize: Tuple[int, int] = None, ax: Optional[matplotlib.axes.Axes] = None) Tuple[matplotlib.figure.Figure, Union[matplotlib.axes.Axes, List[matplotlib.axes.Axes]]][source]¶
Creates a circuit diagram visualization of a schedule using matplotlib. Each gate, pulse, measurement, and operation are plotted in the order of execution, but the exact timing is not visible here.
- Parameters:
schedule – the schedule to render.
figsize – matplotlib figsize.
ax – Axis handle to use for plotting.
- Returns:
fig – matplotlib figure object.
ax – matplotlib axis object.
Example
from quantify_scheduler import Schedule from quantify_scheduler.operations.gate_library import Reset, X90, CZ, Rxy, Measure from quantify_scheduler.visualization.circuit_diagram import circuit_diagram_matplotlib sched = Schedule(f"Bell experiment on q0-q1") sched.add(Reset("q0", "q1")) sched.add(X90("q0")) sched.add(X90("q1"), ref_pt="start", rel_time=0) sched.add(CZ(qC="q0", qT="q1")) sched.add(Rxy(theta=45, phi=0, qubit="q0") ) sched.add(Measure("q0", acq_index=0)) sched.add(Measure("q1", acq_index=0), ref_pt="start") circuit_diagram_matplotlib(sched);
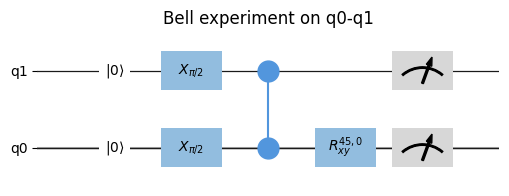
Note
Gates that are started simultaneously on the same qubit will overlap.
from quantify_scheduler import Schedule from quantify_scheduler.operations.gate_library import X90, Measure sched = Schedule(f"overlapping gates") sched.add(X90("q0")) sched.add(Measure("q0"), ref_pt="start", rel_time=0) sched.plot_circuit_diagram();

Note
If the pulse’s port address was not found then the pulse will be plotted on the ‘other’ timeline.