Installation¶
Stable release¶
This is the preferred method to install Quantify, as it will always install the most recent stable release. If you want to contribute to quantify, see [Setting up for local development].
On Windows and macOS (Anaconda)¶
Quantify-core has third party dependencies that can have environment-specific problems. We recommend using the Anaconda Python distribution which works out of the box on most systems.
If you are familiar with software development (package manager, git, terminal, Python, etc.) the following should get you running in no time. Otherwise, follow the [Detailed instructions] and learn a few productivity tips on your way.
Install Anaconda.
Install Quantify (and JupyterLab) in a new conda environment, see also the Conda cheat sheet.
N.B. If you are interested to contribute to Quantify-core and/or Quantify-scheduler you should set them up for local development instead.
$ # run the following commands step by step! $ conda create --name quantify-env python=3.8 $ conda activate quantify-env $ conda install -c conda-forge jupyterlab $ python -m ipykernel install --user --name=quantify-env --display-name="Python 3 Quantify Env" $ pip install quantify-core $ # (Optionally) install quantify-scheduler: $ pip install quantify-scheduler $ jupyter labextension install jupyterlab-plotly --no-build $ # this might take a few minutes $ jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager plotlywidget
You are good to go! Head over to the User guide to get started.
Detailed instructions¶
Install Anaconda.
(Windows only) Install Git BASH to have a unix-like bash terminal (default options during installation should work well on most setups).
Tip
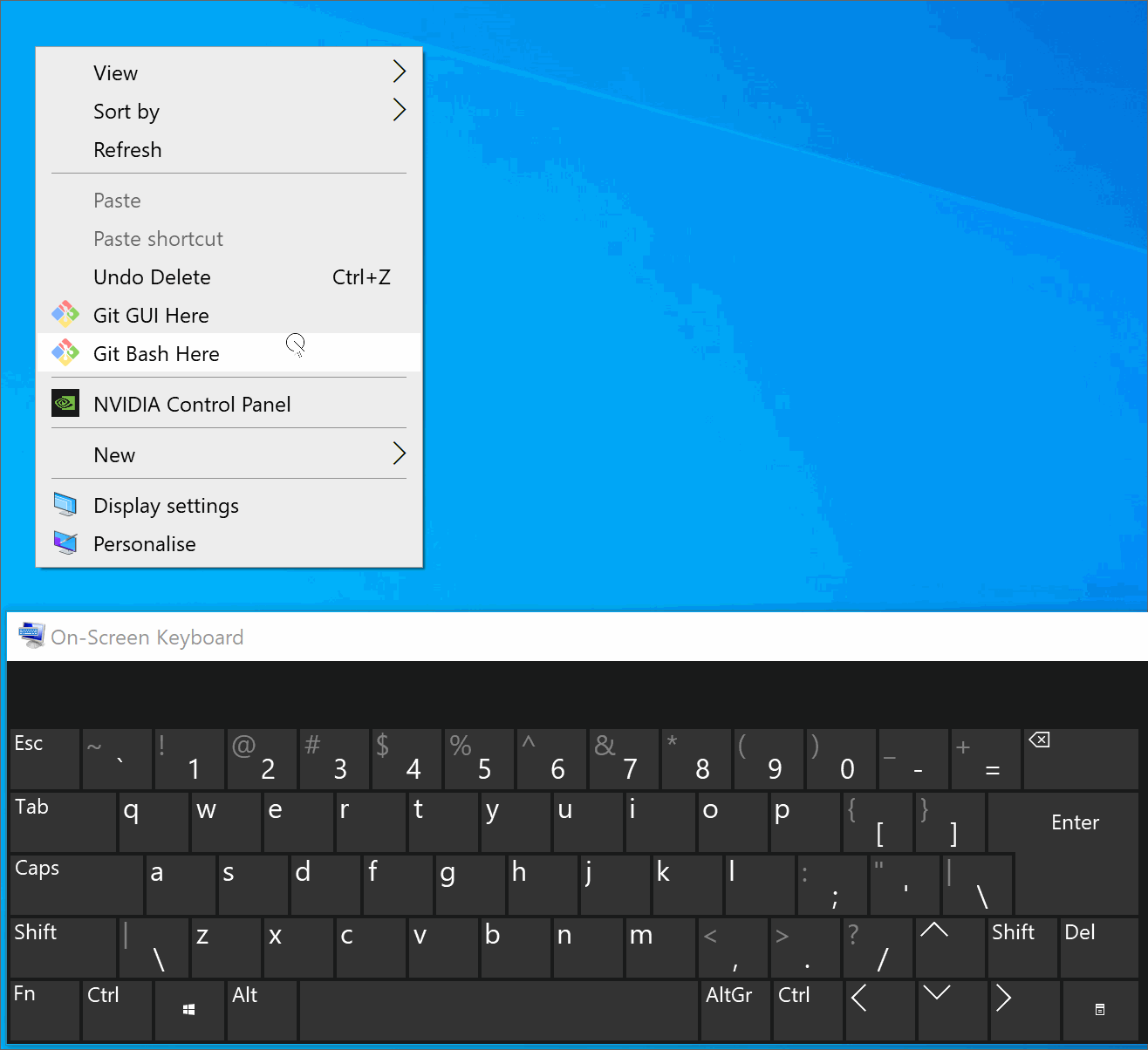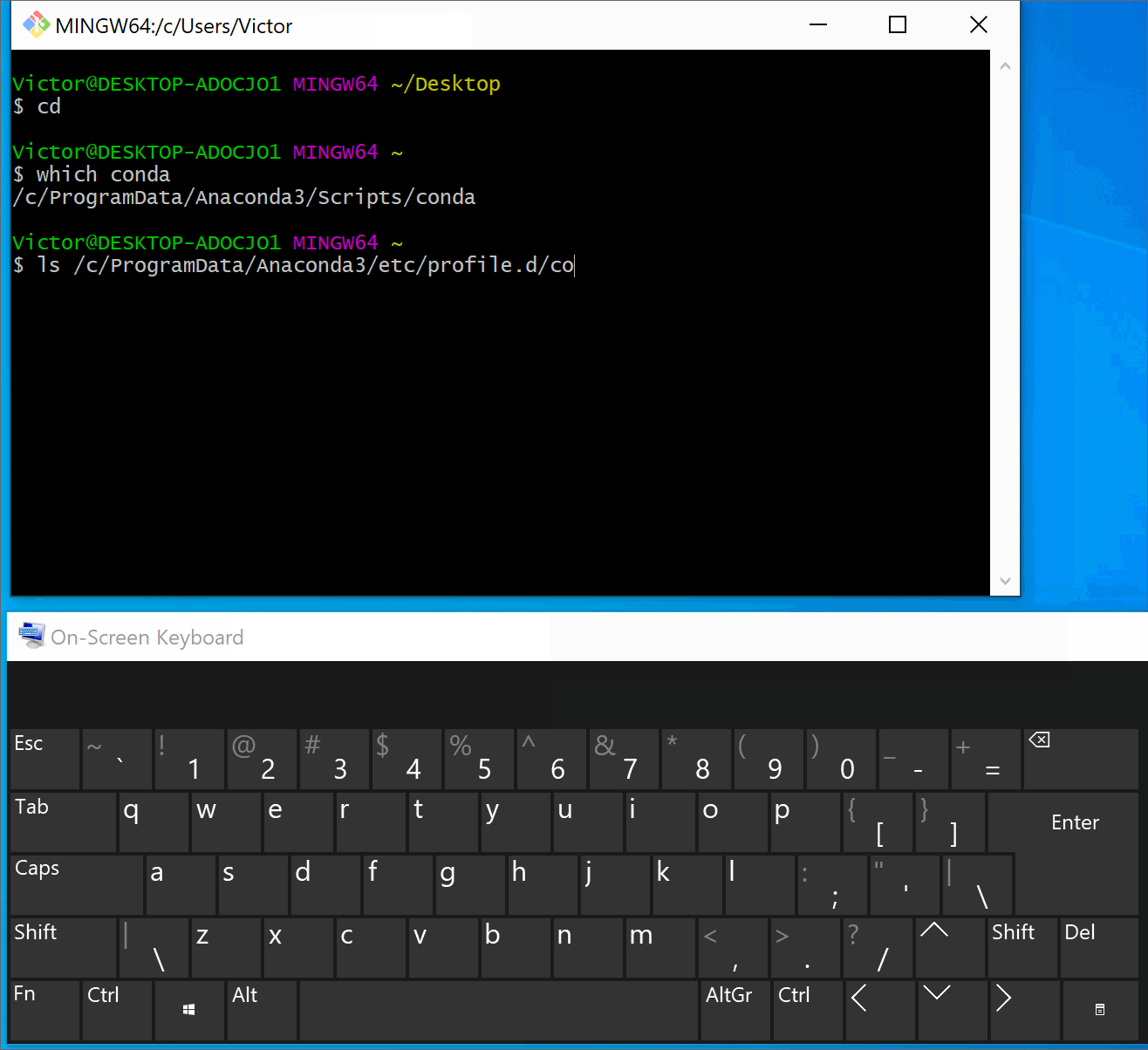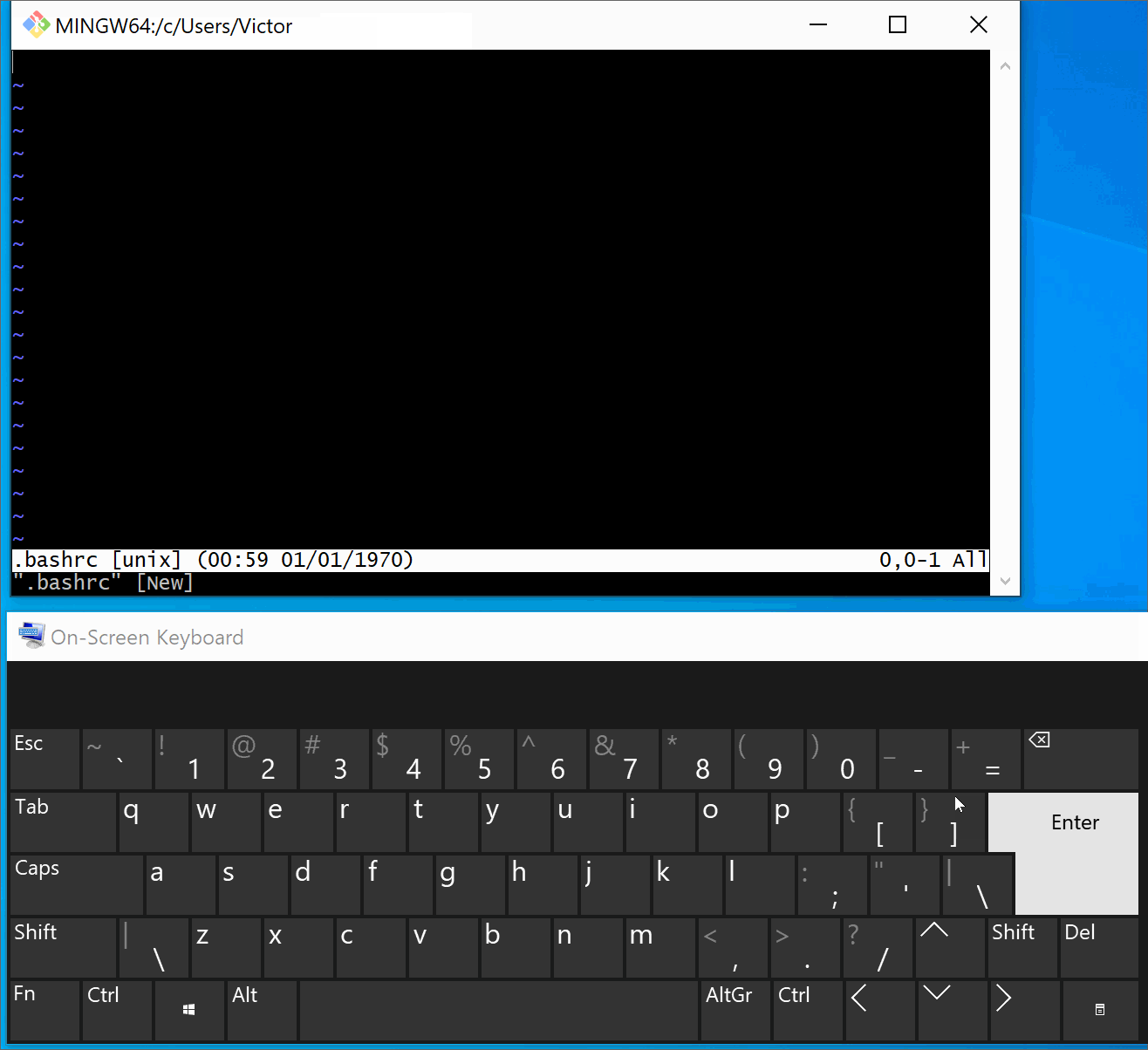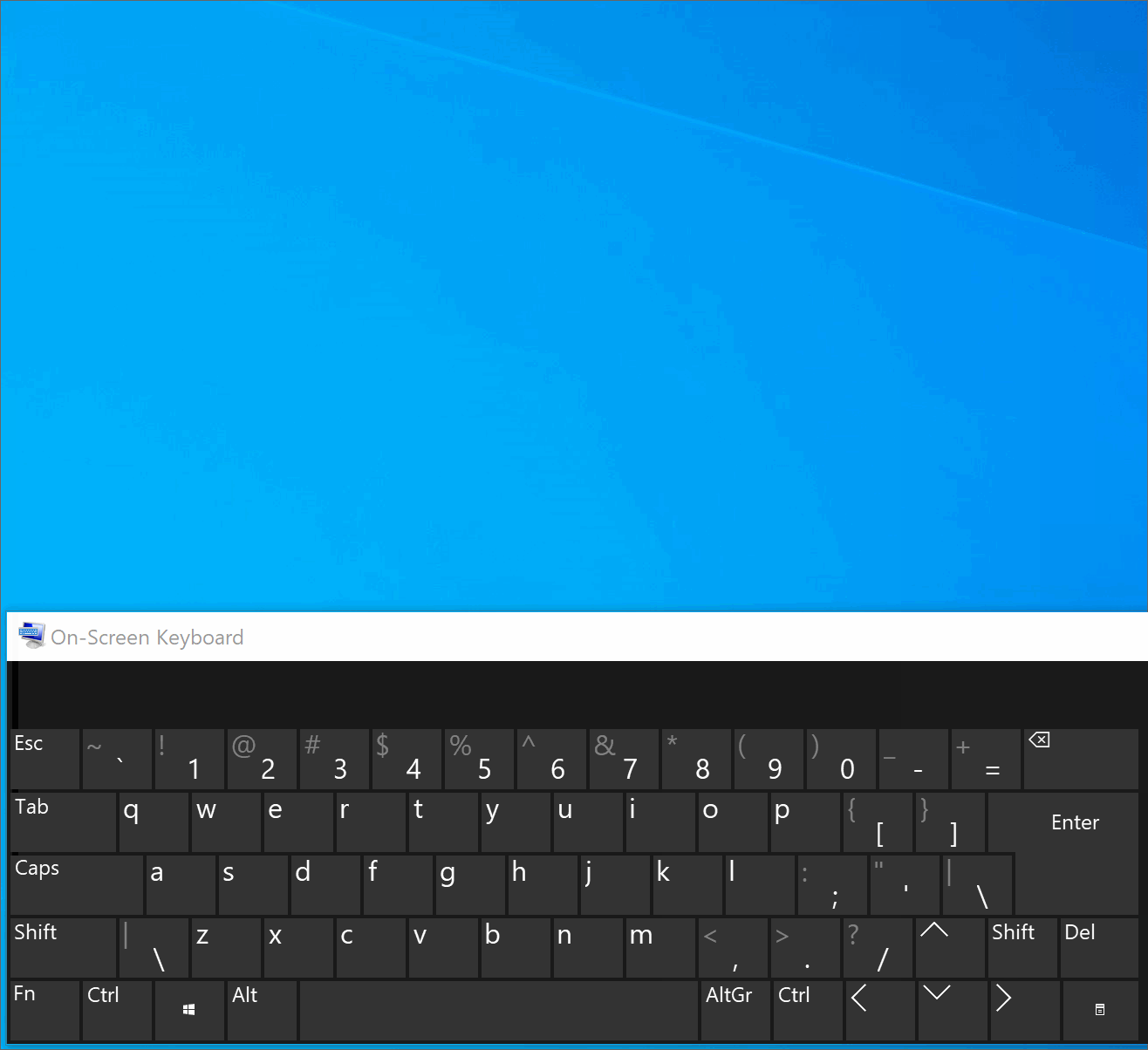
Users can right click any folder in windows and open Git BASH in that location.
Note
Be aware that a unix-like terminal on windows has some caveats. To avoid them, we recommend to run any python code using JupyterLab (installation steps below).
(Windows only) Add
source /path/to/Anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.shin the.bashrc(or in the.bash_profile) to expose the anaconda in bash terminal (see instruction below if you need help).Tip
If you followed the default anaconda installation the path to it will be similar to
/c/Users/<YOUR_USERNAME>/anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.shor/c/ProgramData/Anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh.Pro tip: you can drag and drop a file from the file explorer into the terminal and get the path of the file (instead of typing it manually).
Instructions: expose anaconda in the bash terminal
Below we illustrate this process in Git Bash. You can find detailed step-by-step instructions here.
Note
To confirm you have a functional installation of anaconda, run
condain the terminal. This will print the conda help message which is an indication of a working installation.Create a conda environment, see also the Conda cheat sheet.
$ conda create --name quantify-env python=3.8 # create the conda environment, you can replace `quantify-env` if you wish $ conda activate quantify-env # activates the conda environment
Tip
You can add
conda activate quantify-envat the end of the.bashrc(or.bash_profile) if you wish for this environment to be activated automatically in the terminal when it is opened (see instructions below).Install jupyter-lab in the new environment using:
$ conda install -c conda-forge jupyterlab # install jupyter lab $ # add the environment as an available kernel for jupyter notebook within jupyter-lab. $ python -m ipykernel install --user --name=quantify-env --display-name="Python 3 Quantify Env"
Install quantify-core pypi
If you are interested to contribute to Quantify-core you should set it up for local development instead.
$ pip install quantify-coreNote
We currently do not have a conda recipe for installation, instead we refer to the default pip installation within a conda environment.
(Optionally) install quantify-scheduler
If you are interested to contribute to Quantify-scheduler you should set it up for local development instead. You only need to replace
quantify-corewithquantify-schedulerin the provided commands.$ pip install quantify-scheduler $ jupyter labextension install jupyterlab-plotly --no-build $ # this might take a few minutes $ jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager plotlywidget
Other systems¶
Confirm that you have a compatible working python interpreter by running the following in your terminal of choice:
$ python --version
Python 3.8.10
Exact version may be different, check the list of supported versions in the setup.py file.
Install Quantify:
$ pip install quantify-core
If you don’t have pip installed, this Python installation guide can guide you through the process.
Update to latest version¶
To update quantify to the latest version:
$ pip install --upgrade quantify-core
Setting up for local development¶
Ready to contribute? Here’s how to set up Quantify for local development.
Follow the [Installation] steps for your system skipping the last step (
pip install ...).Fork the
quantify-corerepo on GitLab.Clone your fork locally:
$ git clone git@gitlab.com:your_name_here/quantify-core.gitInstall quantify locally:
$ cd quantify-core/ $ pip install -e . $ pip install -r requirements_dev.txt
(Optional) Install
pre-commitwhich will automatically format the code using black:$ pre-commit installNote
When the code is not well formatted a
git commitwill fail. You only need to run it again. This second time the code will be already black-compliant.Create a branch for local development:
$ git checkout -b name-of-your-bugfix-or-featureNow you can make your changes locally.
To ensure good quality code run pylint on your code and address any reasonable code quality issues. See Editor and IDE integration for tips on how to integrate pylint in your editor or IDE.
When you are done making changes, auto-format the repository with
blackand ensure test coverage$ black . $ pytest --cov
Tip
Running parts of the test suite
To run only parts of the test suite, specify the folder in which to look for tests as an argument to pytest. The following example
$ py.test tests/measurement --cov quantify_core/measurementwill look for tests located in the tests/measurement directory and report test coverage of the quantify_core/measurement module.
Tip
Speed up tests with parallel execution
$ py.test -n 2 # where 2 is the number of cores of your CPU
Building the documentation
If you have worked on documentation or docstrings you need to review how your docs look locally and ensure no error or warnings are raised. You can build the docs locally using:
$ cd docs $ # unix $ make html $ # windows $ ./make.bat html
The docs will be located in
quantify_core/docs/_build.Tip
If you are working on documentation it can be useful to automatically rebuild the docs after every change. This can be done using the
sphinx-autobuildpackage. Through the following command:$ sphinx-autobuild docs docs/_build/htmlThe documentation will then be hosted on
localhost:8000Tip
Building the tutorials can be time consuming, if you are not editing them, feel free to delete your local copy of the
quantify-core/docs/tutorialsto skip their build. You can recover the files using git (do not commit the deleted files).Commit your changes and push your branch to GitLab:
$ git add . $ git commit -m "Your detailed description of your changes." $ git push origin name-of-your-bugfix-or-feature
Review the Merge Request Guidelines and submit a merge request through the GitLab website.
Add short entry in the
CHANGELOG.mdunderUnreleased, commit and push.
Troubleshooting¶
If for some reason you are not able to install or use Quantify using the prescribed ways indicated above, make sure you have working python environment (e.g. you are able to run an IPyhon terminal). Follow the next steps that aim at installing Quantify from source and running its tests.
Uninstall Quantify:
$ pip uninstall quantify-coreInstall from source (run line by line):
$ git clone https://gitlab.com/quantify-os/quantify-core.git; cd quantify-core $ pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager . $ pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager -r requirements_dev.txt $ pytest -v
The tests will either pass or not. In any case, please report your experience and which test do not pass by creating a
New issueon the issue tracker, your efforts are much appreciated and will help us to understand the problems you might be facing.
Downgrade to specific version¶
If for any reason you require a specific version of the package, e.g. 0.3.0, run:
$ pip install --upgrade quantify-core==0.3.0
Potential issues: PyQtGraph and PyQt5¶
Quantify-core has a dependency on the PyQt5 package, which itself has a dependency on the Qt5 runtime. On most systems, the standard installation process will correctly install Qt. The Anaconda installation should resolve issues with installation on Windows or macOS. You may need to consult a search engine if you have a more exotic system.