quantify_core¶
analysis¶
base_analysis¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
cosine_analysis¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
spectroscopy_analysis¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
single_qubit_timedomain¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
interpolation_analysis¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
optimization_analysis¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
fitting_models¶
Models and fit functions to be used with the lmfit fitting framework.
- class CosineModel(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ModelExemplary lmfit model with a guess for a cosine.
Note
The
lmfit.modelsmodule provides several fitting models that might fit your needs out of the box.- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Parameters:
independent_vars (
listofstr) – Arguments to the model function that are independent variables default is['x']).prefix (
str) – String to prepend to parameter names, needed to add two Models that have parameter names in common.nan_policy – How to handle NaN and missing values in data. See Notes below.
**kwargs – Keyword arguments to pass to
Model.
Notes
1. nan_policy sets what to do when a NaN or missing value is seen in the data. Should be one of:
‘raise’ : raise a ValueError (default)
‘propagate’ : do nothing
‘omit’ : drop missing data
See also
- guess(data, x, **kws)[source]¶
Guess starting values for the parameters of a model.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
params (
Parameters) – Initial, guessed values for the parameters of a Model... versionchanged:: 1.0.3 – Argument
xis now explicitly required to estimate starting values.
- class DecayOscillationModel(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ModelModel for a decaying oscillation which decays to a point with 0 offset from the centre of the of the oscillation (as in a Ramsey experiment, for example).
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Parameters:
independent_vars (
listofstr) – Arguments to the model function that are independent variables default is['x']).prefix (
str) – String to prepend to parameter names, needed to add two Models that have parameter names in common.nan_policy – How to handle NaN and missing values in data. See Notes below.
**kwargs – Keyword arguments to pass to
Model.
Notes
1. nan_policy sets what to do when a NaN or missing value is seen in the data. Should be one of:
‘raise’ : raise a ValueError (default)
‘propagate’ : do nothing
‘omit’ : drop missing data
See also
- guess(data, **kws)[source]¶
Guess starting values for the parameters of a model.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
params (
Parameters) – Initial, guessed values for the parameters of a Model... versionchanged:: 1.0.3 – Argument
xis now explicitly required to estimate starting values.
- class ExpDecayModel(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ModelModel for an exponential decay, such as a qubit T1 measurement.
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Parameters:
independent_vars (
listofstr) – Arguments to the model function that are independent variables default is['x']).prefix (
str) – String to prepend to parameter names, needed to add two Models that have parameter names in common.nan_policy – How to handle NaN and missing values in data. See Notes below.
**kwargs – Keyword arguments to pass to
Model.
Notes
1. nan_policy sets what to do when a NaN or missing value is seen in the data. Should be one of:
‘raise’ : raise a ValueError (default)
‘propagate’ : do nothing
‘omit’ : drop missing data
See also
- guess(data, **kws)[source]¶
Guess starting values for the parameters of a model.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
params (
Parameters) – Initial, guessed values for the parameters of a Model... versionchanged:: 1.0.3 – Argument
xis now explicitly required to estimate starting values.
- class RabiModel(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ModelModel for a Rabi oscillation as a function of the microwave drive amplitude. Phase of oscillation is fixed at \(\pi\) in order to ensure that the oscillation is at a minimum when the drive amplitude is 0.
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Parameters:
independent_vars (
listofstr) – Arguments to the model function that are independent variables default is['x']).prefix (
str) – String to prepend to parameter names, needed to add two Models that have parameter names in common.nan_policy – How to handle NaN and missing values in data. See Notes below.
**kwargs – Keyword arguments to pass to
Model.
Notes
1. nan_policy sets what to do when a NaN or missing value is seen in the data. Should be one of:
‘raise’ : raise a ValueError (default)
‘propagate’ : do nothing
‘omit’ : drop missing data
See also
- guess(data, **kws)[source]¶
Guess starting values for the parameters of a model.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
params (
Parameters) – Initial, guessed values for the parameters of a Model... versionchanged:: 1.0.3 – Argument
xis now explicitly required to estimate starting values.
- class ResonatorModel(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ModelResonator model
Implementation and design patterns inspired by the complex resonator model example (lmfit documentation).
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Parameters:
independent_vars (
listofstr) – Arguments to the model function that are independent variables default is['x']).prefix (
str) – String to prepend to parameter names, needed to add two Models that have parameter names in common.nan_policy – How to handle NaN and missing values in data. See Notes below.
**kwargs – Keyword arguments to pass to
Model.
Notes
1. nan_policy sets what to do when a NaN or missing value is seen in the data. Should be one of:
‘raise’ : raise a ValueError (default)
‘propagate’ : do nothing
‘omit’ : drop missing data
See also
- guess(data, **kws)[source]¶
Guess starting values for the parameters of a model.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
params (
Parameters) – Initial, guessed values for the parameters of a Model... versionchanged:: 1.0.3 – Argument
xis now explicitly required to estimate starting values.
- cos_func(x, frequency, amplitude, offset, phase=0)[source]¶
An oscillating cosine function:
\(y = \mathrm{amplitude} \times \cos(2 \pi \times \mathrm{frequency} \times x + \mathrm{phase}) + \mathrm{offset}\)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Output signal magnitude
- exp_damp_osc_func(t, tau, n_factor, frequency, phase, amplitude, offset)[source]¶
A sinusoidal oscillation with an exponentially decaying envelope function:
\(y = \mathrm{amplitude} \times \exp\left(-(t/\tau)^\mathrm{n\_factor}\right)(\cos(2\pi\mathrm{frequency}\times t + \mathrm{phase}) + \mathrm{oscillation_offset}) + \mathrm{exponential_offset}\)
- exp_decay_func(t, tau, amplitude, offset, n_factor)[source]¶
This is a general exponential decay function:
\(y = \mathrm{amplitude} \times \exp\left(-(t/\tau)^\mathrm{n\_factor}\right) + \mathrm{offset}\)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Output of exponential function as a float
- fft_freq_phase_guess(data, t)[source]¶
Guess for a cosine fit using FFT, only works for evenly spaced points.
- get_guess_common_doc()[source]¶
Returns a common docstring to be used for the
guess()method of custom fittingModels.Usage example for a custom fitting model
See the usage example at the end of the
ResonatorModelsource-code:class ResonatorModel(lmfit.model.Model): """ Resonator model Implementation and design patterns inspired by the `complex resonator model example <https://lmfit.github.io/lmfit-py/examples/example_complex_resonator_model.html>`_ (`lmfit` documentation). """ # pylint: disable=line-too-long # pylint: disable=empty-docstring # pylint: disable=abstract-method def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # pass in the defining equation so the user doesn't have to later. super().__init__(hanger_func_complex_SI, *args, **kwargs) self.set_param_hint("Ql", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive self.set_param_hint("Qe", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive # Internal and coupled quality factor can be derived from fitted params self.set_param_hint("Qi", expr="1./(1./Ql-1./Qe*cos(theta))", vary=False) self.set_param_hint("Qc", expr="Qe/cos(theta)", vary=False) # pylint: disable=too-many-locals # pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring def guess(self, data, **kws) -> lmfit.parameter.Parameters: f = kws.get("f", None) if f is None: return None argmin_s21 = np.abs(data).argmin() fmin = f.min() fmax = f.max() # guess that the resonance is the lowest point fr_guess = f[argmin_s21] # assume the user isn't trying to fit just a small part of a resonance curve. Q_min = 0.1 * (fr_guess / (fmax - fmin)) delta_f = np.diff(f) # assume f is sorted min_delta_f = delta_f[delta_f > 0].min() Q_max = ( fr_guess / min_delta_f ) # assume data actually samples the resonance reasonably Q_guess = np.sqrt(Q_min * Q_max) # geometric mean, why not? (phi_0_guess, phi_v_guess) = resonator_phase_guess( data, f ) # Come up with a guess for phase velocity self.set_param_hint("fr", value=fr_guess, min=fmin, max=fmax) self.set_param_hint("Ql", value=Q_guess * 1.01, min=Q_min, max=Q_max) self.set_param_hint("Qe", value=Q_guess * 0.99, min=0) self.set_param_hint("A", value=np.mean(abs(data)), min=0) # The parameters below need a proper guess. self.set_param_hint("theta", value=0, min=-np.pi / 2, max=np.pi / 2) self.set_param_hint("phi_0", value=phi_0_guess) self.set_param_hint("phi_v", value=phi_v_guess) self.set_param_hint("alpha", value=0, min=-1, max=1) params = self.make_params() return lmfit.models.update_param_vals(params, self.prefix, **kws) # Same design patter is used in lmfit.models __init__.__doc__ = get_model_common_doc() + mk_seealso("hanger_func_complex_SI") guess.__doc__ = get_guess_common_doc()
- get_model_common_doc()[source]¶
Returns a common docstring to be used with custom fitting
Models.Usage example for a custom fitting model
See the usage example at the end of the
ResonatorModelsource-code:class ResonatorModel(lmfit.model.Model): """ Resonator model Implementation and design patterns inspired by the `complex resonator model example <https://lmfit.github.io/lmfit-py/examples/example_complex_resonator_model.html>`_ (`lmfit` documentation). """ # pylint: disable=line-too-long # pylint: disable=empty-docstring # pylint: disable=abstract-method def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # pass in the defining equation so the user doesn't have to later. super().__init__(hanger_func_complex_SI, *args, **kwargs) self.set_param_hint("Ql", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive self.set_param_hint("Qe", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive # Internal and coupled quality factor can be derived from fitted params self.set_param_hint("Qi", expr="1./(1./Ql-1./Qe*cos(theta))", vary=False) self.set_param_hint("Qc", expr="Qe/cos(theta)", vary=False) # pylint: disable=too-many-locals # pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring def guess(self, data, **kws) -> lmfit.parameter.Parameters: f = kws.get("f", None) if f is None: return None argmin_s21 = np.abs(data).argmin() fmin = f.min() fmax = f.max() # guess that the resonance is the lowest point fr_guess = f[argmin_s21] # assume the user isn't trying to fit just a small part of a resonance curve. Q_min = 0.1 * (fr_guess / (fmax - fmin)) delta_f = np.diff(f) # assume f is sorted min_delta_f = delta_f[delta_f > 0].min() Q_max = ( fr_guess / min_delta_f ) # assume data actually samples the resonance reasonably Q_guess = np.sqrt(Q_min * Q_max) # geometric mean, why not? (phi_0_guess, phi_v_guess) = resonator_phase_guess( data, f ) # Come up with a guess for phase velocity self.set_param_hint("fr", value=fr_guess, min=fmin, max=fmax) self.set_param_hint("Ql", value=Q_guess * 1.01, min=Q_min, max=Q_max) self.set_param_hint("Qe", value=Q_guess * 0.99, min=0) self.set_param_hint("A", value=np.mean(abs(data)), min=0) # The parameters below need a proper guess. self.set_param_hint("theta", value=0, min=-np.pi / 2, max=np.pi / 2) self.set_param_hint("phi_0", value=phi_0_guess) self.set_param_hint("phi_v", value=phi_v_guess) self.set_param_hint("alpha", value=0, min=-1, max=1) params = self.make_params() return lmfit.models.update_param_vals(params, self.prefix, **kws) # Same design patter is used in lmfit.models __init__.__doc__ = get_model_common_doc() + mk_seealso("hanger_func_complex_SI") guess.__doc__ = get_guess_common_doc()
- hanger_func_complex_SI(f, fr, Ql, Qe, A, theta, phi_v, phi_0, alpha=1)[source]¶
This is the complex function for a hanger (lambda/4 resonator).
- Parameters:
Qe (
floatfloat) – magnitude of extrinsic quality factorQe = |Q_extrinsic|theta (
floatfloat) – phase of extrinsic quality factor (in rad)phi_v (
floatfloat) – phase to account for propagation delay to samplephi_0 (
floatfloat) – phase to account for propagation delay from samplealpha (
floatfloat(default:1)) – slope of signal around the resonance
- Return type:
- Returns:
complex valued transmission
See eq. S4 from Bruno et al. (2015) ArXiv:1502.04082.
\[S_{21} = A \left(1+\alpha \frac{f-f_r}{f_r} \right) \left(1- \frac{\frac{Q_l}{|Q_e|}e^{i\theta} }{1+2iQ_l \frac{f-f_r}{f_r}} \right) e^{i (\phi_v f + \phi_0)}\]The loaded and extrinsic quality factors are related to the internal and coupled Q according to:
\[\frac{1}{Q_l} = \frac{1}{Q_c}+\frac{1}{Q_i}\]and
\[\frac{1}{Q_c} = \mathrm{Re}\left(\frac{1}{|Q_e|e^{-i\theta}}\right)\]
- mk_seealso(function_name, role='func', prefix='\\n\\n', module_location='.')[source]¶
Returns a sphinx seealso pointing to a function.
Intended to be used for building custom fitting model docstrings.
Usage example for a custom fitting model
See the usage example at the end of the
ResonatorModelsource-code:class ResonatorModel(lmfit.model.Model): """ Resonator model Implementation and design patterns inspired by the `complex resonator model example <https://lmfit.github.io/lmfit-py/examples/example_complex_resonator_model.html>`_ (`lmfit` documentation). """ # pylint: disable=line-too-long # pylint: disable=empty-docstring # pylint: disable=abstract-method def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # pass in the defining equation so the user doesn't have to later. super().__init__(hanger_func_complex_SI, *args, **kwargs) self.set_param_hint("Ql", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive self.set_param_hint("Qe", min=0) # Enforce Q is positive # Internal and coupled quality factor can be derived from fitted params self.set_param_hint("Qi", expr="1./(1./Ql-1./Qe*cos(theta))", vary=False) self.set_param_hint("Qc", expr="Qe/cos(theta)", vary=False) # pylint: disable=too-many-locals # pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring def guess(self, data, **kws) -> lmfit.parameter.Parameters: f = kws.get("f", None) if f is None: return None argmin_s21 = np.abs(data).argmin() fmin = f.min() fmax = f.max() # guess that the resonance is the lowest point fr_guess = f[argmin_s21] # assume the user isn't trying to fit just a small part of a resonance curve. Q_min = 0.1 * (fr_guess / (fmax - fmin)) delta_f = np.diff(f) # assume f is sorted min_delta_f = delta_f[delta_f > 0].min() Q_max = ( fr_guess / min_delta_f ) # assume data actually samples the resonance reasonably Q_guess = np.sqrt(Q_min * Q_max) # geometric mean, why not? (phi_0_guess, phi_v_guess) = resonator_phase_guess( data, f ) # Come up with a guess for phase velocity self.set_param_hint("fr", value=fr_guess, min=fmin, max=fmax) self.set_param_hint("Ql", value=Q_guess * 1.01, min=Q_min, max=Q_max) self.set_param_hint("Qe", value=Q_guess * 0.99, min=0) self.set_param_hint("A", value=np.mean(abs(data)), min=0) # The parameters below need a proper guess. self.set_param_hint("theta", value=0, min=-np.pi / 2, max=np.pi / 2) self.set_param_hint("phi_0", value=phi_0_guess) self.set_param_hint("phi_v", value=phi_v_guess) self.set_param_hint("alpha", value=0, min=-1, max=1) params = self.make_params() return lmfit.models.update_param_vals(params, self.prefix, **kws) # Same design patter is used in lmfit.models __init__.__doc__ = get_model_common_doc() + mk_seealso("hanger_func_complex_SI") guess.__doc__ = get_guess_common_doc()
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
resulting string
calibration¶
Module containing analysis utilities for calibration procedures.
In particular, manipulation of data and calibration points for qubit readout calibration.
- has_calibration_points(s21, indices_state_0=(-2,), indices_state_1=(-1,))[source]¶
Attempts to determine if the provided complex S21 data has calibration points for the ground and first excited states of qubit.
In this ideal scenario, if the datapoints indicated by the indices correspond to the calibration points, then these points will be located on the extremities of a “segment” on the IQ plane.
Three pieces of information are used to infer the presence of calibration points:
The angle of the calibration points with respect to the average of the datapoints,
The distance between the calibration points, and
The average distance to the line defined be the calibration points.
The detection is made robust by averaging 3 datapoints for each extremity of the “segment” described by the data on the IQ-plane.
Examples
In these examples this function is able to correctly predict the presence of the calibrations in both cases.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from quantify_core.analysis.calibration import has_calibration_points from quantify_core.utilities.examples_support import mk_iq_shots def _with_cal(data_): return np.concatenate((data_, (center_0, center_1))) def _print(ax_, data_): ax_.set_title( f"W/out cal.: {has_calibration_points(data_)}\n" f"With cal.: {has_calibration_points(_with_cal(data_))}" ) fig, ((ax0, ax1), (ax2, ax3)) = plt.subplots( 2, 2, figsize=(10, 10 / 1.6), sharex=True, sharey=True ) center_0, center_1, center_2 = 0.6 + 1.2j, -0.2 + 0.5j, 0 + 1.5j NUM_SHOTS = 50 data = mk_iq_shots( NUM_SHOTS, sigmas=[0.1] * 2, centers=(center_0, center_1), probabilities=[0.3, 1 - 0.3], ) ax0.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") _print(ax0, data) data = mk_iq_shots( NUM_SHOTS, sigmas=[0.1] * 3, centers=(center_0, center_1, center_2), probabilities=[0.35, 0.35, 1 - 0.35 - 0.35], ) ax1.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") _print(ax1, data) data = mk_iq_shots( NUM_SHOTS, sigmas=[0.1], centers=(center_0,), probabilities=[1], ) ax2.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") _print(ax2, data) data = np.fromiter( ( mk_iq_shots( NUM_SHOTS * 2, sigmas=[0.5] * 2, centers=(center_0, center_1), probabilities=[prob, 1 - prob], ).mean() for prob in np.linspace(0, 1, 35) ), dtype=complex, ) ax3.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") _print(ax3, data) for i, ax in enumerate(fig.axes): ax.plot(center_0.real, center_0.imag, "^", label="|0>", markersize=10) ax.plot(center_1.real, center_1.imag, "d", label="|1>", markersize=10) if i == 1: ax.plot(center_2.real, center_2.imag, "*", label="|2>", markersize=10) ax.legend()
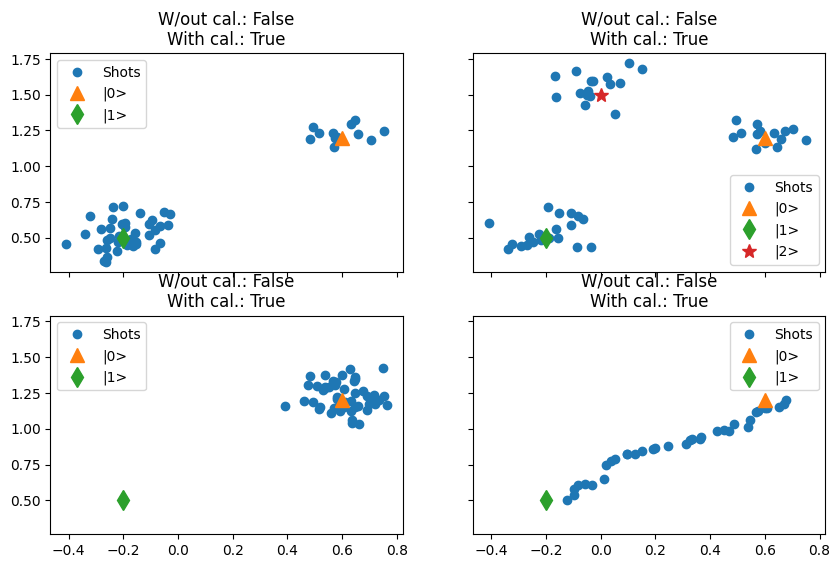
- Parameters:
s21 (
ndarrayndarray) – Array of complex datapoints corresponding to the experiment on the IQ plane.indices_state_0 (
tupletuple(default:(-2,))) – Indices in thes21array that correspond to the ground state.indices_state_1 (
tupletuple(default:(-1,))) – Indices in thes21array that correspond to the first excited state.
- Return type:
- Returns:
The inferred presence of calibration points.
data¶
types¶
Module containing the core data concepts of quantify.
- class TUID(value: str)[source]¶
A human readable unique identifier based on the timestamp. This class does not wrap the passed in object but simply verifies and returns it.
A tuid is a string formatted as
YYYYmmDD-HHMMSS-sss-******. The tuid serves as a unique identifier for experiments in quantify.See also
The.
handlingmodule.- classmethod is_valid(tuid)[source]¶
Test if tuid is valid. A valid tuid is a string formatted as
YYYYmmDD-HHMMSS-sss-******.- Parameters:
tuid (str) – a tuid string
- Returns:
True if the string is a valid TUID.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – Invalid format
handling¶
Utilities for handling data.
- concat_dataset(tuids, dim='dim_0')[source]¶
This function takes in a list of TUIDs and concatenates the corresponding datasets. It adds the TUIDs as a coordinate in the new dataset.
- create_exp_folder(tuid, name='', datadir=None)[source]¶
Creates an empty folder to store an experiment container.
If the folder already exists, simply returns the experiment folder corresponding to the
TUID.- Parameters:
- Returns:
Full path of the experiment folder following format:
/datadir/YYYYmmDD/YYYYmmDD-HHMMSS-sss-******-name/.
- default_datadir(verbose=True)[source]¶
Returns (and optionally print) a default datadir path.
Intended for fast prototyping, tutorials, examples, etc..
- extract_parameter_from_snapshot(snapshot, parameter)[source]¶
A function which takes a parameter and extracts it from a snapshot, including in the case where the parameter is part of a nested submodule within a QCoDeS instrument
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The dict specifying the parameter properties which was extracted from the snapshot
- Return type:
parameter_dict
- get_datadir()[source]¶
Returns the current data directory. The data directory can be changed using
set_datadir().
- get_latest_tuid(contains='')[source]¶
Returns the most recent tuid.
Tip
This function is similar to
get_tuids_containing()but is preferred if one is only interested in the most recentTUIDfor performance reasons.- Parameters:
contains (
strstr(default:'')) – An optional string contained in the experiment name.- Return type:
- Returns:
The latest TUID.
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – No data found.
- get_tuids_containing(contains, t_start=None, t_stop=None, max_results=9223372036854775807, reverse=False)[source]¶
Returns a list of tuids containing a specific label.
Tip
If one is only interested in the most recent
TUID,get_latest_tuid()is preferred for performance reasons.- Parameters:
contains (
strstr) – A string contained in the experiment name.t_start (
datetime|str|NoneUnion[datetime,str,None] (default:None)) – datetime to search from, inclusive. If a string is specified, it will be converted to a datetime object usingparse. If no value is specified, will use the year 1 as a reference t_start.t_stop (
datetime|str|NoneUnion[datetime,str,None] (default:None)) – datetime to search until, exclusive. If a string is specified, it will be converted to a datetime object usingparse. If no value is specified, will use the current time as a reference t_stop.max_results (
intint(default:9223372036854775807)) – Maximum number of results to return. Defaults to unlimited.reverse (
boolbool(default:False)) – If False, sorts tuids chronologically, if True sorts by most recent.
- Returns:
A list of
TUID: objects.- Return type:
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – No data found.
- get_varying_parameter_values(tuids, parameter)[source]¶
A function that gets a parameter which varies over multiple experiments and puts it in a ndarray.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
The values of the varying parameter.
- initialize_dataset(settable_pars, setpoints, gettable_pars)[source]¶
Initialize an empty dataset based on settable_pars, setpoints and gettable_pars
- load_dataset(tuid, datadir=None, name='dataset.hdf5')[source]¶
Loads a dataset specified by a tuid.
Tip
This method also works when specifying only the first part of a
TUID.Note
This method uses
load_dataset()to ensure the file is closed after loading as datasets are intended to be immutable after performing the initial experiment.- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
The dataset.
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – No data found for specified date.
- load_dataset_from_path(path)[source]¶
Loads a
Datasetwith a specific engine preference.Before returning the dataset
AdapterH5NetCDF.recover()is applied.This function tries to load the dataset until success with the following engine preference:
"h5netcdf""netcdf4"No engine specified (
load_dataset()default)
- load_processed_dataset(tuid, analysis_name)[source]¶
Given an experiment TUID and the name of an analysis previously run on it, retrieves the processed dataset resulting from that analysis.
- load_quantities_of_interest(tuid, analysis_name)[source]¶
Given an experiment TUID and the name of an analysis previously run on it, retrieves the corresponding “quantities of interest” data.
- load_snapshot(tuid, datadir=None, list_to_ndarray=False, file='snapshot.json')[source]¶
Loads a snapshot specified by a tuid.
- Parameters:
tuid (
TUIDTUID) – ATUIDstring. It is also possible to specify only the first part of a tuid.datadir (
str|NoneOptional[str] (default:None)) – Path of the data directory. IfNone, usesget_datadir()to determine the data directory.list_to_ndarray (
boolbool(default:False)) – Uses an internal DecodeToNumpy decoder which allows a user to automatically convert a list to numpy array during deserialization of the snapshot.file (
strstr(default:'snapshot.json')) – Filename to load.
- Return type:
- Returns:
The snapshot.
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – No data found for specified date.
- locate_experiment_container(tuid, datadir=None)[source]¶
Returns the path to the experiment container of the specified tuid.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
The path to the experiment container
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – Experiment container not found.
- multi_experiment_data_extractor(experiment, parameter, *, new_name=None, t_start=None, t_stop=None)[source]¶
A data extraction function which loops through multiple quantify data directories and extracts the selected varying parameter value and corresponding datasets, then compiles this data into a single dataset for further analysis.
- Parameters:
experiment (
strstr) – The experiment to be included in the new dataset. For example “Pulsed spectroscopy”instrument – The name of the instrument from which to get the value. For example “fluxcurrent”
parameter (
strstr) – The name and address of the QCoDeS parameter from which to get the value, including the instrument name and all submodules. For example"current_source.module0.dac0.current".new_name (
str|NoneOptional[str] (default:None)) – The name of the new multifile dataset. If no new name is given, it will create a new name as experiment vs instrument.t_start (
str|NoneOptional[str] (default:None)) – Datetime to search from, inclusive. If a string is specified, it will be converted to a datetime object usingparse. If no value is specified, will use the year 1 as a reference t_start.t_stop (
str|NoneOptional[str] (default:None)) – Datetime to search until, exclusive. If a string is specified, it will be converted to a datetime object usingparse. If no value is specified, will use the current time as a reference t_stop.
- Return type:
- Returns:
The compiled quantify dataset.
- snapshot(update=False, clean=True)[source]¶
State of all instruments setup as a JSON-compatible dictionary (everything that the custom JSON encoder class
qcodes.utils.helpers.NumpyJSONEncodersupports).
- to_gridded_dataset(quantify_dataset, dimension='dim_0', coords_names=None)[source]¶
Converts a flattened (a.k.a. “stacked”) dataset as the one generated by the
initialize_dataset()to a dataset in which the measured values are mapped onto a grid in the xarray format.This will be meaningful only if the data itself corresponds to a gridded measurement.
Note
Each individual
(x0[i], x1[i], x2[i], ...)setpoint must be unique.Conversions applied:
The names
"x0", "x1", ...will correspond to the names of the Dimensions.- The unique values for each of the
x0, x1, ...Variables are converted to Coordinates.
- The unique values for each of the
- The
y0, y1, ...Variables are reshaped into a (multi-)dimensional grid and associated to the Coordinates.
- The
See also
MeasurementControl.setpoints_grid()- Parameters:
quantify_dataset (
DatasetDataset) – Input dataset in the format generated by theinitialize_dataset.dimension (
strstr(default:'dim_0')) – The flattened xarray Dimension.coords_names (
Iterable|NoneOptional[Iterable] (default:None)) – Optionally specify explicitly which Variables correspond to orthogonal coordinates, e.g. datasets holds values for("x0", "x1")but only “x0” is independent:to_gridded_dataset(dset, coords_names=["x0"]).
- Return type:
- Returns:
The new dataset.
Examples
from pathlib import Path import numpy as np from qcodes import ManualParameter, Parameter, validators from quantify_core.data.handling import set_datadir, to_gridded_dataset from quantify_core.measurement import MeasurementControl set_datadir(Path.home() / "quantify-data") time_a = ManualParameter( name="time_a", label="Time A", unit="s", vals=validators.Numbers(), initial_value=1 ) time_b = ManualParameter( name="time_b", label="Time B", unit="s", vals=validators.Numbers(), initial_value=1 ) signal = Parameter( name="sig_a", label="Signal A", unit="V", get_cmd=lambda: np.exp(time_a()) + 0.5 * np.exp(time_b()), ) meas_ctrl = MeasurementControl("meas_ctrl") meas_ctrl.settables([time_a, time_b]) meas_ctrl.gettables(signal) meas_ctrl.setpoints_grid([np.linspace(0, 5, 10), np.linspace(5, 0, 12)]) dset = meas_ctrl.run("2D-single-float-valued-settable-gettable") dset_grid = to_gridded_dataset(dset) dset_grid.y0.plot(cmap="viridis")
Starting iterative measurement... 100% completed | elapsed time: 0s | time left: 0s 100% completed | elapsed time: 0s | time left: 0s
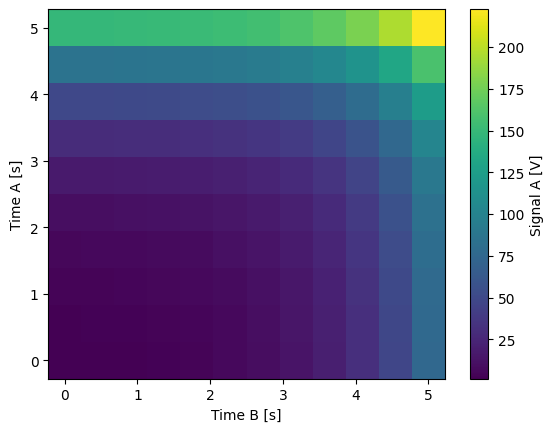
- trim_dataset(dataset)[source]¶
Trim NaNs from a dataset, useful in the case of a dynamically resized dataset (e.g. adaptive loops).
- write_dataset(path, dataset)[source]¶
Writes a
Datasetto a file with the h5netcdf engine.Before writing the
AdapterH5NetCDF.adapt()is applied.To accommodate for complex-type numbers and arrays
invalid_netcdf=Trueis used.
dataset_adapters¶
Utilities for dataset (python object) handling.
- class AdapterH5NetCDF[source]¶
Quantify dataset adapter for the
h5netcdfengine.It has the functionality of adapting the Quantify dataset to a format compatible with the
h5netcdfxarray backend engine that is used to write and load the dataset to/from disk.Warning
The
h5netcdfengine has minor issues when performing a two-way trip of the dataset. Thetypeof some attributes are not preserved. E.g., list- and tuple-like objects are loaded as numpy arrays ofdtype=object.- classmethod adapt(dataset)[source]¶
Serializes to JSON the dataset and variables attributes.
To prevent the JSON serialization for specific items, their names should be listed under the attribute named
json_serialize_exclude(for eachattrsdictionary).
- static attrs_convert(attrs, inplace=False, vals_converter=<function dumps>)[source]¶
Converts to/from JSON string the values of the keys which are not listed in the
json_serialize_excludelist.
- class DatasetAdapterBase[source]¶
A generic interface for a dataset adapter.
Note
It might be difficult to grasp the generic purpose of this class. See
AdapterH5NetCDFfor a specialized use case.A dataset adapter is intended to “adapt”/”convert” a dataset to a format compatible with some other piece of software such as a function, interface, read/write back end, etc.. The main use case is to define the interface of the
AdapterH5NetCDFthat converts the Quantify dataset for loading and writing to/from disk.Subclasses implementing this interface are intended to be a two-way bridge to some other object/interface/backend to which we refer to as the “Target” of the adapter.
The function
.adapt()should return a dataset to be consumed by the Target.The function
.recover()should receive a dataset generated by the Target.
- class DatasetAdapterIdentity[source]¶
A dataset adapter that does not modify the datasets in any way.
Intended to be used just as an object that respects the adapter interface defined by
DatasetAdapterBase.A particular use case is the backwards compatibility for loading and writing older versions of the Quantify dataset.
dataset_attrs¶
Utilities for handling the attributes of xarray.Dataset and
xarray.DataArray (python objects) handling.
- class QCoordAttrs(unit='', long_name='', is_main_coord=None, uniformly_spaced=None, is_dataset_ref=False, json_serialize_exclude=<factory>)[source]¶
A dataclass representing the
attrsattribute of main and secondary coordinates.All attributes are mandatory to be present but can be
None.Examples
from quantify_core.utilities import examples_support examples_support.mk_main_coord_attrs()
{ 'unit': '', 'long_name': '', 'is_main_coord': True, 'uniformly_spaced': True, 'is_dataset_ref': False, 'json_serialize_exclude': [] }
examples_support.mk_secondary_coord_attrs()
{ 'unit': '', 'long_name': '', 'is_main_coord': False, 'uniformly_spaced': True, 'is_dataset_ref': False, 'json_serialize_exclude': [] }
- is_dataset_ref: bool = False¶
Flags if it is an array of
quantify_core.data.types.TUIDs of other dataset.
- is_main_coord: bool = None¶
When set to
True, flags the xarray coordinate to correspond to a main coordinate, otherwise (False) it corresponds to a secondary coordinate.
- class QDatasetAttrs(tuid=None, dataset_name='', dataset_state=None, timestamp_start=None, timestamp_end=None, quantify_dataset_version='2.0.0', software_versions=<factory>, relationships=<factory>, json_serialize_exclude=<factory>)[source]¶
A dataclass representing the
attrsattribute of the Quantify dataset.All attributes are mandatory to be present but can be
None.Example
import pendulum from quantify_core.utilities import examples_support examples_support.mk_dataset_attrs( dataset_name="Bias scan", timestamp_start=pendulum.now().to_iso8601_string(), timestamp_end=pendulum.now().add(minutes=2).to_iso8601_string(), dataset_state="done", )
{ 'tuid': '20230926-194319-105-0cb49b', 'dataset_name': 'Bias scan', 'dataset_state': 'done', 'timestamp_start': '2023-09-26T19:43:19.105681+02:00', 'timestamp_end': '2023-09-26T19:45:19.105717+02:00', 'quantify_dataset_version': '2.0.0', 'software_versions': {}, 'relationships': [], 'json_serialize_exclude': [] }
- dataset_name: str = ''¶
The dataset name, usually same as the the experiment name included in the name of the experiment container.
- dataset_state: Literal[None, 'running', 'interrupted (safety)', 'interrupted (forced)', 'done'] = None¶
Denotes the last known state of the experiment/data acquisition that served to ‘build’ this dataset. Can be used later to filter ‘bad’ datasets.
- json_serialize_exclude: List[str] = ()¶
A list of strings corresponding to the names of other attributes that should not be json-serialized when writing the dataset to disk. Empty by default.
- quantify_dataset_version: str = '2.0.0'¶
A string identifying the version of this Quantify dataset for backwards compatibility.
- relationships: List[QDatasetIntraRelationship] = ()¶
A list of relationships within the dataset specified as list of dictionaries that comply with the
QDatasetIntraRelationship.
- software_versions: Dict[str, str] = ()¶
A mapping of other relevant software packages that are relevant to log for this dataset. Another example is the git tag or hash of a commit of a lab repository.
Example
import pendulum from quantify_core.utilities import examples_support examples_support.mk_dataset_attrs( dataset_name="My experiment", timestamp_start=pendulum.now().to_iso8601_string(), timestamp_end=pendulum.now().add(minutes=2).to_iso8601_string(), software_versions={ "lab_fridge_magnet_driver": "v1.4.2", # software version/tag "my_lab_repo": "9d8acf63f48c469c1b9fa9f2c3cf230845f67b18", # git commit hash }, )
{ 'tuid': '20230926-194319-117-1f6198', 'dataset_name': 'My experiment', 'dataset_state': None, 'timestamp_start': '2023-09-26T19:43:19.117450+02:00', 'timestamp_end': '2023-09-26T19:45:19.117486+02:00', 'quantify_dataset_version': '2.0.0', 'software_versions': { 'lab_fridge_magnet_driver': 'v1.4.2', 'my_lab_repo': '9d8acf63f48c469c1b9fa9f2c3cf230845f67b18' }, 'relationships': [], 'json_serialize_exclude': [] }
- timestamp_end: Optional[str] = None¶
Human-readable timestamp (ISO8601) as returned by
pendulum.now().to_iso8601_string()(docs). Specifies when the experiment/data acquisition ended.
- timestamp_start: Optional[str] = None¶
Human-readable timestamp (ISO8601) as returned by
pendulum.now().to_iso8601_string()(docs). Specifies when the experiment/data acquisition started.
- tuid: Optional[str] = None¶
The time-based unique identifier of the dataset. See
quantify_core.data.types.TUID.
- class QDatasetIntraRelationship(item_name=None, relation_type=None, related_names=<factory>, relation_metadata=<factory>)[source]¶
A dataclass representing a dictionary that specifies a relationship between dataset variables.
A prominent example are calibration points contained within one variable or several variables that are necessary to interpret correctly the data of another variable.
Examples
This is how the attributes of a dataset containing a
q0main variable andq0_calsecondary variables would look like. Theq0_calcorresponds to calibrations datapoints. See Quantify dataset - examples for examples with more context.from quantify_core.data.dataset_attrs import QDatasetIntraRelationship from quantify_core.utilities import examples_support attrs = examples_support.mk_dataset_attrs( relationships=[ QDatasetIntraRelationship( item_name="q0", relation_type="calibration", related_names=["q0_cal"], ).to_dict() ] )
- item_name: str = None¶
The name of the coordinate/variable to which we want to relate other coordinates/variables.
A list of names related to the
item_name.
- class QVarAttrs(unit='', long_name='', is_main_var=None, uniformly_spaced=None, grid=None, is_dataset_ref=False, has_repetitions=False, json_serialize_exclude=<factory>)[source]¶
A dataclass representing the
attrsattribute of main and secondary variables.All attributes are mandatory to be present but can be
None.Examples
from quantify_core.utilities import examples_support examples_support.mk_main_var_attrs(coords=["time"])
{ 'unit': '', 'long_name': '', 'is_main_var': True, 'uniformly_spaced': True, 'grid': True, 'is_dataset_ref': False, 'has_repetitions': False, 'json_serialize_exclude': [], 'coords': ['time'] }
examples_support.mk_secondary_var_attrs(coords=["cal"])
{ 'unit': '', 'long_name': '', 'is_main_var': False, 'uniformly_spaced': True, 'grid': True, 'is_dataset_ref': False, 'has_repetitions': False, 'json_serialize_exclude': [], 'coords': ['cal'] }
- grid: Optional[bool] = None¶
Indicates if the variables data are located on a grid, which does not need to be uniformly spaced along all dimensions. In other words, specifies if the corresponding main coordinates are the ‘unrolled’ points (also known as ‘unstacked’) corresponding to a grid.
If
Truethan it is possible to usequantify_core.data.handling.to_gridded_dataset()to convert the variables to a ‘stacked’ version.
- has_repetitions: bool = False¶
Indicates that the outermost dimension of this variable is a repetitions dimension. This attribute is intended to allow easy programmatic detection of such dimension. It can be used, for example, to average along this dimension before an automatic live plotting or analysis.
- is_dataset_ref: bool = False¶
Flags if it is an array of
quantify_core.data.types.TUIDs of other dataset. See also Dataset for a “nested MeasurementControl” experiment.
- is_main_var: bool = None¶
When set to
True, flags this xarray data variable to correspond to a main variable, otherwise (False) it corresponds to a secondary variable.
- json_serialize_exclude: List[str] = ()¶
A list of strings corresponding to the names of other attributes that should not be json-serialized when writing the dataset to disk. Empty by default.
- get_main_coords(dataset)[source]¶
Finds the main coordinates in the dataset (except secondary coordinates).
Finds the xarray coordinates in the dataset that have their attributes
is_main_coordset toTrue(inside thexarray.DataArray.attrsdictionary).
- get_main_dims(dataset)[source]¶
Determines the ‘main’ dimensions in the dataset.
Each of the dimensions returned is the outermost dimension for an main coordinate/variable, OR the second one when a repetitions dimension is present. (see
has_repetitions).These dimensions are detected based on
is_main_coordandis_main_varattributes.Warning
The dimensions listed in this list should be considered “incompatible” in the sense that the main coordinate/variables must lie on one and only one of such dimension.
Note
The dimensions, on which the secondary coordinates/variables lie, are not included in this list. See also
get_secondary_dims().
- get_main_vars(dataset)[source]¶
Finds the main variables in the dataset (except secondary variables).
Finds the xarray data variables in the dataset that have their attributes
is_main_varset toTrue(inside thexarray.DataArray.attrsdictionary).
- get_secondary_coords(dataset)[source]¶
Finds the secondary coordinates in the dataset.
Finds the xarray coordinates in the dataset that have their attributes
is_main_coordset toFalse(inside thexarray.DataArray.attrsdictionary).
- get_secondary_dims(dataset)[source]¶
Returns the ‘main’ secondary dimensions.
For details see
get_main_dims(),is_main_varandis_main_coord.
- get_secondary_vars(dataset)[source]¶
Finds the secondary variables in the dataset.
Finds the xarray data variables in the dataset that have their attributes
is_main_varset toFalse(inside thexarray.DataArray.attrsdictionary).
experiment¶
Utilities for managing experiment data.
- class QuantifyExperiment(tuid, dataset=None)[source]¶
Class which represents all data related to an experiment. This allows the user to run experiments and store data without the quantify_core.measurement.control.MeasurementControl. The class serves as an initial interface for other data storage backends.
- load_dataset()[source]¶
Loads the quantify dataset associated with the TUID set within the class.
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – If no file with a dataset can be found
- Return type:
- load_text(rel_path)[source]¶
Loads a string from a text file from the path specified by ~.experiment_directory / rel_path.
- Parameters:
rel_path (
strstr) – path relative to the base directory of the experiment, e.g. “data.json” or “my_folder/data.txt”- Return type:
- Returns:
The loaded text from disk
- Raises:
FileNotFoundError – If no file can be found at rel_path
- save_metadata(metadata=None)[source]¶
Writes the metadata to disk as specified by ~.experiment_directory.
- save_snapshot(snapshot=None)[source]¶
Writes the snapshot to disk as specified by ~.experiment_directory.
- save_text(text, rel_path)[source]¶
Saves a string to a text file in the path specified by ~.experiment_directory / rel_path.
measurement¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
types¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
control¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
utilities¶
experiment_helpers¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
dataset_examples¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
examples_support¶
Utilities used for creating examples for docs/tutorials/tests.
- mk_cosine_instrument()[source]¶
A container of parameters (mock instrument) providing a cosine model.
- Return type:
InstrumentInstrument
- mk_dataset_attrs(tuid=<function gen_tuid>, **kwargs)[source]¶
A factory of attributes for Quantify dataset.
See
QDatasetAttrsfor details.
- mk_iq_shots(num_shots=128, sigmas=(0.1, 0.1), centers=(-0.2 + 0.65j, 0.7 + 4j), probabilities=(0.4, 0.6), seed=112233)[source]¶
Generates clusters of (I + 1j*Q) points with a Gaussian distribution with the specified sigmas and centers according to the probabilities of each cluster
Examples
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from quantify_core.utilities.examples_support import mk_iq_shots center_0, center_1, center_2 = 0.6 + 1.2j, -0.2 + 0.5j, 0 + 1.5j data = mk_iq_shots( 100, sigmas=[0.1] * 2, centers=(center_0, center_1), probabilities=[0.3, 1 - 0.3] ) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") ax.plot(center_0.real, center_0.imag, "^", label="|0>", markersize=10) ax.plot(center_1.real, center_1.imag, "d", label="|1>", markersize=10) _ = ax.legend() data = mk_iq_shots( 200, sigmas=[0.1] * 3, centers=(center_0, center_1, center_2), probabilities=[0.35, 0.35, 1 - 0.35 - 0.35], ) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(data.real, data.imag, "o", label="Shots") ax.plot(center_0.real, center_0.imag, "^", label="|0>", markersize=10) ax.plot(center_1.real, center_1.imag, "d", label="|1>", markersize=10) ax.plot(center_2.real, center_2.imag, "*", label="|2>", markersize=10) _ = ax.legend()
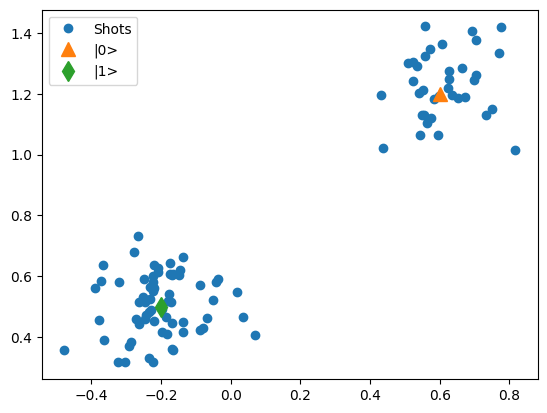
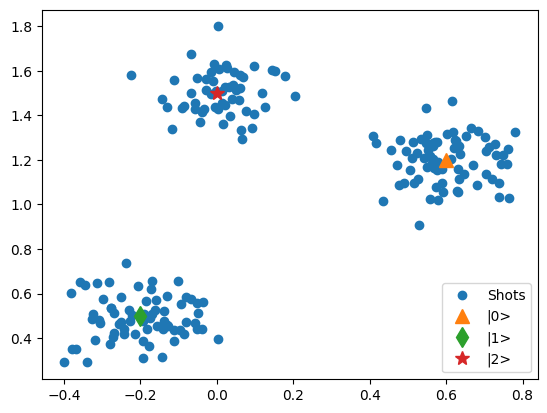
- Parameters:
num_shots (
intint(default:128)) – The number of shot to generate.sigma – The sigma of the Gaussian distribution used for both real and imaginary parts.
centers (
Tuple[complex] |ndarrayUnion[Tuple[complex],ndarray] (default:((-0.2+0.65j), (0.7+4j)))) – The center of each cluster on the imaginary plane.probabilities (
Tuple[float] |ndarrayUnion[Tuple[float],ndarray] (default:(0.4, 0.6))) – The probabilities of each cluster being randomly selected for each shot.seed (
int|NoneOptional[int] (default:112233)) – Random number generator seed passed tonumpy.random.default_rng.
- Return type:
- mk_main_coord_attrs(uniformly_spaced=True, is_main_coord=True, **kwargs)[source]¶
A factory of attributes for main coordinates.
See
QCoordAttrsfor details.- Parameters:
uniformly_spaced (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QCoordAttrs.uniformly_spaced.is_main_coord (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QCoordAttrs.is_main_coord.**kwargs – Any other items used to update the output dictionary.
- Return type:
- mk_main_var_attrs(grid=True, uniformly_spaced=True, is_main_var=True, has_repetitions=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
A factory of attributes for main variables.
See
QVarAttrsfor details.- Parameters:
grid (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.grid.uniformly_spaced (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.uniformly_spaced.is_main_var (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.is_main_var.has_repetitions (
boolbool(default:False)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.has_repetitions.**kwargs – Any other items used to update the output dictionary.
- Return type:
- mk_secondary_coord_attrs(uniformly_spaced=True, is_main_coord=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
A factory of attributes for secondary coordinates.
See
QCoordAttrsfor details.- Parameters:
uniformly_spaced (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QCoordAttrs.uniformly_spaced.is_main_coord (
boolbool(default:False)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QCoordAttrs.is_main_coord.**kwargs – Any other items used to update the output dictionary.
- Return type:
- mk_secondary_var_attrs(grid=True, uniformly_spaced=True, is_main_var=False, has_repetitions=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
A factory of attributes for secondary variables.
See
QVarAttrsfor details.- Parameters:
grid (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.grid.uniformly_spaced (
boolbool(default:True)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.uniformly_spaced.is_main_var (
boolbool(default:False)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.is_main_var.has_repetitions (
boolbool(default:False)) – Seequantify_core.data.dataset_attrs.QVarAttrs.has_repetitions.**kwargs – Any other items used to update the output dictionary.
- Return type:
- mk_surface7_sched(num_cycles=3)[source]¶
Generates a schedule with some of the feature of a Surface 7 experiment as portrayed in Fig. 4b of [Marques et al., 2021].
- mk_trace_for_iq_shot(iq_point, time_values=array([0.00e+00, 1.00e-09, 2.00e-09, 3.00e-09, 4.00e-09, 5.00e-09, 6.00e-09, 7.00e-09, 8.00e-09, 9.00e-09, 1.00e-08, 1.10e-08, 1.20e-08, 1.30e-08, 1.40e-08, 1.50e-08, 1.60e-08, 1.70e-08, 1.80e-08, 1.90e-08, 2.00e-08, 2.10e-08, 2.20e-08, 2.30e-08, 2.40e-08, 2.50e-08, 2.60e-08, 2.70e-08, 2.80e-08, 2.90e-08, 3.00e-08, 3.10e-08, 3.20e-08, 3.30e-08, 3.40e-08, 3.50e-08, 3.60e-08, 3.70e-08, 3.80e-08, 3.90e-08, 4.00e-08, 4.10e-08, 4.20e-08, 4.30e-08, 4.40e-08, 4.50e-08, 4.60e-08, 4.70e-08, 4.80e-08, 4.90e-08, 5.00e-08, 5.10e-08, 5.20e-08, 5.30e-08, 5.40e-08, 5.50e-08, 5.60e-08, 5.70e-08, 5.80e-08, 5.90e-08, 6.00e-08, 6.10e-08, 6.20e-08, 6.30e-08, 6.40e-08, 6.50e-08, 6.60e-08, 6.70e-08, 6.80e-08, 6.90e-08, 7.00e-08, 7.10e-08, 7.20e-08, 7.30e-08, 7.40e-08, 7.50e-08, 7.60e-08, 7.70e-08, 7.80e-08, 7.90e-08, 8.00e-08, 8.10e-08, 8.20e-08, 8.30e-08, 8.40e-08, 8.50e-08, 8.60e-08, 8.70e-08, 8.80e-08, 8.90e-08, 9.00e-08, 9.10e-08, 9.20e-08, 9.30e-08, 9.40e-08, 9.50e-08, 9.60e-08, 9.70e-08, 9.80e-08, 9.90e-08, 1.00e-07, 1.01e-07, 1.02e-07, 1.03e-07, 1.04e-07, 1.05e-07, 1.06e-07, 1.07e-07, 1.08e-07, 1.09e-07, 1.10e-07, 1.11e-07, 1.12e-07, 1.13e-07, 1.14e-07, 1.15e-07, 1.16e-07, 1.17e-07, 1.18e-07, 1.19e-07, 1.20e-07, 1.21e-07, 1.22e-07, 1.23e-07, 1.24e-07, 1.25e-07, 1.26e-07, 1.27e-07, 1.28e-07, 1.29e-07, 1.30e-07, 1.31e-07, 1.32e-07, 1.33e-07, 1.34e-07, 1.35e-07, 1.36e-07, 1.37e-07, 1.38e-07, 1.39e-07, 1.40e-07, 1.41e-07, 1.42e-07, 1.43e-07, 1.44e-07, 1.45e-07, 1.46e-07, 1.47e-07, 1.48e-07, 1.49e-07, 1.50e-07, 1.51e-07, 1.52e-07, 1.53e-07, 1.54e-07, 1.55e-07, 1.56e-07, 1.57e-07, 1.58e-07, 1.59e-07, 1.60e-07, 1.61e-07, 1.62e-07, 1.63e-07, 1.64e-07, 1.65e-07, 1.66e-07, 1.67e-07, 1.68e-07, 1.69e-07, 1.70e-07, 1.71e-07, 1.72e-07, 1.73e-07, 1.74e-07, 1.75e-07, 1.76e-07, 1.77e-07, 1.78e-07, 1.79e-07, 1.80e-07, 1.81e-07, 1.82e-07, 1.83e-07, 1.84e-07, 1.85e-07, 1.86e-07, 1.87e-07, 1.88e-07, 1.89e-07, 1.90e-07, 1.91e-07, 1.92e-07, 1.93e-07, 1.94e-07, 1.95e-07, 1.96e-07, 1.97e-07, 1.98e-07, 1.99e-07, 2.00e-07, 2.01e-07, 2.02e-07, 2.03e-07, 2.04e-07, 2.05e-07, 2.06e-07, 2.07e-07, 2.08e-07, 2.09e-07, 2.10e-07, 2.11e-07, 2.12e-07, 2.13e-07, 2.14e-07, 2.15e-07, 2.16e-07, 2.17e-07, 2.18e-07, 2.19e-07, 2.20e-07, 2.21e-07, 2.22e-07, 2.23e-07, 2.24e-07, 2.25e-07, 2.26e-07, 2.27e-07, 2.28e-07, 2.29e-07, 2.30e-07, 2.31e-07, 2.32e-07, 2.33e-07, 2.34e-07, 2.35e-07, 2.36e-07, 2.37e-07, 2.38e-07, 2.39e-07, 2.40e-07, 2.41e-07, 2.42e-07, 2.43e-07, 2.44e-07, 2.45e-07, 2.46e-07, 2.47e-07, 2.48e-07, 2.49e-07, 2.50e-07, 2.51e-07, 2.52e-07, 2.53e-07, 2.54e-07, 2.55e-07, 2.56e-07, 2.57e-07, 2.58e-07, 2.59e-07, 2.60e-07, 2.61e-07, 2.62e-07, 2.63e-07, 2.64e-07, 2.65e-07, 2.66e-07, 2.67e-07, 2.68e-07, 2.69e-07, 2.70e-07, 2.71e-07, 2.72e-07, 2.73e-07, 2.74e-07, 2.75e-07, 2.76e-07, 2.77e-07, 2.78e-07, 2.79e-07, 2.80e-07, 2.81e-07, 2.82e-07, 2.83e-07, 2.84e-07, 2.85e-07, 2.86e-07, 2.87e-07, 2.88e-07, 2.89e-07, 2.90e-07, 2.91e-07, 2.92e-07, 2.93e-07, 2.94e-07, 2.95e-07, 2.96e-07, 2.97e-07, 2.98e-07, 2.99e-07]), intermediate_freq=50000000.0)[source]¶
Generates mock “traces” that a physical instrument would digitize for the readout of a transmon qubit when using a down-converting IQ mixer.
Examples
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from quantify_core.utilities.examples_support import mk_trace_for_iq_shot, mk_trace_time SHOT = 0.6 + 1.2j time = mk_trace_time() trace = mk_trace_for_iq_shot(SHOT) fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 12 / 1.61 / 2)) _ = ax.plot(time * 1e6, trace.imag, ".-", label="I-quadrature") _ = ax.plot(time * 1e6, trace.real, ".-", label="Q-quadrature") _ = ax.set_xlabel("Time [µs]") _ = ax.set_ylabel("Amplitude [V]") _ = ax.legend()
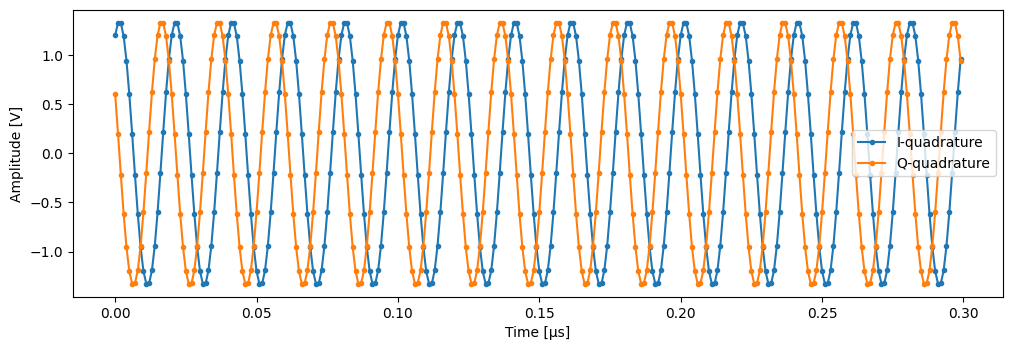
- Parameters:
iq_point (
complexcomplex) – A complex number representing a point on the IQ-plane.time_values (
ndarrayndarray(default:array([0.00e+00, 1.00e-09, 2.00e-09, 3.00e-09, 4.00e-09, 5.00e-09, 6.00e-09, 7.00e-09, 8.00e-09, 9.00e-09, 1.00e-08, 1.10e-08, 1.20e-08, 1.30e-08, 1.40e-08, 1.50e-08, 1.60e-08, 1.70e-08, 1.80e-08, 1.90e-08, 2.00e-08, 2.10e-08, 2.20e-08, 2.30e-08, 2.40e-08, 2.50e-08, 2.60e-08, 2.70e-08, 2.80e-08, 2.90e-08, 3.00e-08, 3.10e-08, 3.20e-08, 3.30e-08, 3.40e-08, 3.50e-08, 3.60e-08, 3.70e-08, 3.80e-08, 3.90e-08, 4.00e-08, 4.10e-08, 4.20e-08, 4.30e-08, 4.40e-08, 4.50e-08, 4.60e-08, 4.70e-08, 4.80e-08, 4.90e-08, 5.00e-08, 5.10e-08, 5.20e-08, 5.30e-08, 5.40e-08, 5.50e-08, 5.60e-08, 5.70e-08, 5.80e-08, 5.90e-08, 6.00e-08, 6.10e-08, 6.20e-08, 6.30e-08, 6.40e-08, 6.50e-08, 6.60e-08, 6.70e-08, 6.80e-08, 6.90e-08, 7.00e-08, 7.10e-08, 7.20e-08, 7.30e-08, 7.40e-08, 7.50e-08, 7.60e-08, 7.70e-08, 7.80e-08, 7.90e-08, 8.00e-08, 8.10e-08, 8.20e-08, 8.30e-08, 8.40e-08, 8.50e-08, 8.60e-08, 8.70e-08, 8.80e-08, 8.90e-08, 9.00e-08, 9.10e-08, 9.20e-08, 9.30e-08, 9.40e-08, 9.50e-08, 9.60e-08, 9.70e-08, 9.80e-08, 9.90e-08, 1.00e-07, 1.01e-07, 1.02e-07, 1.03e-07, 1.04e-07, 1.05e-07, 1.06e-07, 1.07e-07, 1.08e-07, 1.09e-07, 1.10e-07, 1.11e-07, 1.12e-07, 1.13e-07, 1.14e-07, 1.15e-07, 1.16e-07, 1.17e-07, 1.18e-07, 1.19e-07, 1.20e-07, 1.21e-07, 1.22e-07, 1.23e-07, 1.24e-07, 1.25e-07, 1.26e-07, 1.27e-07, 1.28e-07, 1.29e-07, 1.30e-07, 1.31e-07, 1.32e-07, 1.33e-07, 1.34e-07, 1.35e-07, 1.36e-07, 1.37e-07, 1.38e-07, 1.39e-07, 1.40e-07, 1.41e-07, 1.42e-07, 1.43e-07, 1.44e-07, 1.45e-07, 1.46e-07, 1.47e-07, 1.48e-07, 1.49e-07, 1.50e-07, 1.51e-07, 1.52e-07, 1.53e-07, 1.54e-07, 1.55e-07, 1.56e-07, 1.57e-07, 1.58e-07, 1.59e-07, 1.60e-07, 1.61e-07, 1.62e-07, 1.63e-07, 1.64e-07, 1.65e-07, 1.66e-07, 1.67e-07, 1.68e-07, 1.69e-07, 1.70e-07, 1.71e-07, 1.72e-07, 1.73e-07, 1.74e-07, 1.75e-07, 1.76e-07, 1.77e-07, 1.78e-07, 1.79e-07, 1.80e-07, 1.81e-07, 1.82e-07, 1.83e-07, 1.84e-07, 1.85e-07, 1.86e-07, 1.87e-07, 1.88e-07, 1.89e-07, 1.90e-07, 1.91e-07, 1.92e-07, 1.93e-07, 1.94e-07, 1.95e-07, 1.96e-07, 1.97e-07, 1.98e-07, 1.99e-07, 2.00e-07, 2.01e-07, 2.02e-07, 2.03e-07, 2.04e-07, 2.05e-07, 2.06e-07, 2.07e-07, 2.08e-07, 2.09e-07, 2.10e-07, 2.11e-07, 2.12e-07, 2.13e-07, 2.14e-07, 2.15e-07, 2.16e-07, 2.17e-07, 2.18e-07, 2.19e-07, 2.20e-07, 2.21e-07, 2.22e-07, 2.23e-07, 2.24e-07, 2.25e-07, 2.26e-07, 2.27e-07, 2.28e-07, 2.29e-07, 2.30e-07, 2.31e-07, 2.32e-07, 2.33e-07, 2.34e-07, 2.35e-07, 2.36e-07, 2.37e-07, 2.38e-07, 2.39e-07, 2.40e-07, 2.41e-07, 2.42e-07, 2.43e-07, 2.44e-07, 2.45e-07, 2.46e-07, 2.47e-07, 2.48e-07, 2.49e-07, 2.50e-07, 2.51e-07, 2.52e-07, 2.53e-07, 2.54e-07, 2.55e-07, 2.56e-07, 2.57e-07, 2.58e-07, 2.59e-07, 2.60e-07, 2.61e-07, 2.62e-07, 2.63e-07, 2.64e-07, 2.65e-07, 2.66e-07, 2.67e-07, 2.68e-07, 2.69e-07, 2.70e-07, 2.71e-07, 2.72e-07, 2.73e-07, 2.74e-07, 2.75e-07, 2.76e-07, 2.77e-07, 2.78e-07, 2.79e-07, 2.80e-07, 2.81e-07, 2.82e-07, 2.83e-07, 2.84e-07, 2.85e-07, 2.86e-07, 2.87e-07, 2.88e-07, 2.89e-07, 2.90e-07, 2.91e-07, 2.92e-07, 2.93e-07, 2.94e-07, 2.95e-07, 2.96e-07, 2.97e-07, 2.98e-07, 2.99e-07]))) – The time instants at which the mock intermediate-frequency signal is sampled.intermediate_freq (
floatfloat(default:50000000.0)) – The intermediate frequency used in the down-conversion scheme.
- Return type:
- Returns:
An array of complex numbers.
- mk_trace_time(sampling_rate=1000000000.0, duration=3e-07)[source]¶
Generates a
arangein which the entries correspond to time instants up todurationseconds sampled according tosampling_ratein Hz.See
mk_trace_for_iq_shot()for an usage example.
deprecation¶
Utilities used to maintain deprecation and reverse-compatibility of the code.
- deprecated(drop_version, message_or_alias)[source]¶
A decorator for deprecating classes and methods.
For each deprecation we must provide a version when this function or class will be removed completely and an instruction to a user about how to port their existing code to a new software version. This is easily done using this decorator.
If callable is passed instead of a message, this decorator assumes that the function or class has moved to another module and generates the standard instruction to use a new function or class. There is no need to re-implement the function logic in two places, since the implementation of new function or class is used in both new and old aliases.
Example
@deprecated("99.99", 'Initialize the "foo" literal directly.') def get_foo(): return "foo" with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w: warnings.simplefilter("always") get_foo() # issues deprecation warning. assert len(w) == 1 assert w[0].category is DeprecationWarning print(w[0].message)
Function __main__.get_foo() is deprecated and will be removed in --main---99.99. Initialize the "foo" literal directly.
class NewClass: """A very useful class""" def __init__(self, val): self._val = val def val(self): return self._val @deprecated("99.99", NewClass) class OldClass: pass with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w: warnings.simplefilter("always") obj = OldClass(42) # type: ignore assert len(w) == 1 assert w[0].category is DeprecationWarning print(w[0].message) print("obj.val() =", obj.val()) # type: ignore
Class __main__.OldClass is deprecated and will be removed in --main---99.99. Use __main__.NewClass instead. obj.val() = 42
class SomeClass: """A very useful class""" def __init__(self, val): self._val = val def val(self): return self._val @deprecated("7.77", val) def get_val(self): """Deprecated alias""" with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w: warnings.simplefilter("always") val = SomeClass(42).get_val() # issues deprecation warning. assert len(w) == 1 assert w[0].category is DeprecationWarning print(w[0].message) print("obj.get_val() =", val)
Function __main__.SomeClass.get_val() is deprecated and will be removed in --main---7.77. Use __main__.SomeClass.val() instead. obj.get_val() = 42
- Parameters:
drop_version (
strstr) – A version of the package when the deprecated function or class will be dropped.message_or_alias (
str|CallableUnion[str,Callable]) – Either an instruction about how to port the software to a new version without the usage of deprecated calls (string), or the new drop-in replacement to the deprecated class or function (callable).
- Return type:
visualization¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
instrument_monitor¶
Module containing the pyqtgraph based plotting monitor.
- class InstrumentMonitor(name, window_size=(600, 600), remote=True, update_interval=5)[source]¶
Creates a pyqtgraph widget that displays the instrument monitor window.
Example
from quantify_core.measurement import MeasurementControl from quantify_core.visualization import InstrumentMonitor meas_ctrl = MeasurementControl("meas_ctrl") instrument_monitor = InstrumentMonitor("instrument_monitor") # Set True if you want to query the instruments about each parameter # before updating the window. Can be slow due to communication overhead. instrument_monitor.update_snapshot(False)
- __init__(name, window_size=(600, 600), remote=True, update_interval=5)[source]¶
Initializes the pyqtgraph window.
- Parameters:
name – name of the
InstrumentMonitorobject.window_size (
tupletuple(default:(600, 600))) – The size of theInstrumentMonitorwindow in px.remote (
boolbool(default:True)) – Switch to use a remote instance of the pyqtgraph class.update_interval (
intint(default:5)) – Interval in seconds between two updates
- close()[source]¶
(Modified from Instrument class)
Irreversibly stop this instrument and free its resources.
Subclasses should override this if they have other specific resources to close.
- create_widget(window_size=(1000, 600))[source]¶
Saves an instance of the
quantify_core.visualization.ins_mon_widget.qc_snapshot_widget.QcSnapshotWidgetclass during startup. Creates thesnapshottree to display within the remote widget window.- Parameters:
window_size (
tupletuple(default:(1000, 600))) – The size of theInstrumentMonitorwindow in px.
- update_interval = Parameter( get_cmd=self._get_update_interval, set_cmd=self._set_update_interval, unit="s", initial_value=update_interval, vals=vals.Numbers(min_value=0.001), name="update_interval", instrument=self, )¶
Only update the window if this amount of time has passed since the last update.
- update_snapshot = ManualParameter( initial_value=False, vals=vals.Bool(), name="update_snapshot", instrument=self, )¶
Set to True in order to query the instruments about each parameter before updating the window. Can be slow due to communication overhead.
pyqt_plotmon¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
color_utilities¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
mpl_plotting¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
plot_interpolation¶
Built-in immutable sequence.
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple. If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable’s items.
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
SI Utilities¶
Utilities for managing SI units with plotting systems.
- SI_prefix_and_scale_factor(val, unit=None)[source]¶
Takes in a value and unit, returns a scale factor and scaled unit. It returns a scale factor to convert the input value to a value in the range [1.0, 1000.0), plus the corresponding scaled SI unit (e.g. ‘mT’, ‘kV’), deduced from the input unit, to represent the input value in those scaled units.
The scaling is only applied if the unit is an unscaled or scaled unit present in the variable :data::SI_UNITS.
If the unit is None, no scaling is done. If the unit is “SI_PREFIX_ONLY”, the value is scaled and an SI prefix is applied without a base unit.
- SI_val_to_msg_str(val, unit=None, return_type=<class 'str'>)[source]¶
Takes in a value with optional unit and returns a string tuple consisting of (value_str, unit) where the value and unit are rescaled according to SI prefixes, IF the unit is an SI unit (according to the comprehensive list of SI units in this file ;).
the value_str is of the type specified in return_type (str) by default.
- adjust_axeslabels_SI(ax)[source]¶
Auto adjust the labels of a plot generated by xarray to SI-unit aware labels.
- format_value_string(par_name, parameter, end_char='', unit=None)[source]¶
Format an lmfit parameter or uncertainties ufloat to a string of value with uncertainty.
If there is no stderr, use 5 significant figures. If there is a standard error use a precision one order of magnitude more precise than the size of the error and display the stderr itself to two significant figures in standard index notation in the same units as the value.
- Parameters:
par_name (
strstr) – the name of the parameter to use in the stringparameter (
lmfit.parameter.Parameter,) –uncertainties.core.Variableor float. AParameterobject or an object e.g., returned byuncertainties.ufloat(). The value and stderr of this parameter will be used. If a float is given, the stderr is taken to be None.end_char – A character that will be put at the end of the line.
unit – a unit. If this is an SI unit it will be used in automatically determining a prefix for the unit and rescaling accordingly.
- Return type:
- Returns:
The parameter and its error formatted as a string
- set_cbarlabel(cbar, label, unit=None, **kw)[source]¶
Add a unit aware z-label to a colorbar object
- Parameters:
cbar – colorbar object to set label on
label – the desired label
unit – the unit
**kw – keyword argument to be passed to cbar.set_label
- set_xlabel(axis, label, unit=None, **kw)[source]¶
Add a unit aware x-label to an axis object.
- Parameters:
axis – matplotlib axis object to set label on
label – the desired label
unit – the unit
**kw – keyword argument to be passed to matplotlib.set_xlabel
- set_ylabel(axis, label, unit=None, **kw)[source]¶
Add a unit aware y-label to an axis object.
- Parameters:
axis – matplotlib axis object to set label on
label – the desired label
unit – the unit
**kw – keyword argument to be passed to matplotlib.set_ylabel
- value_precision(val, stderr=None)[source]¶
Calculate the precision to which a parameter is to be specified, according to its standard error. Returns the appropriate format specifier string.
If there is no stderr, use 5 significant figures. If there is a standard error use a precision one order of magnitude more precise than the size of the error and display the stderr itself to two significant figures in standard index notation in the same units as the value.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
val_format_specifier (str) – python format specifier which sets the precision of the parameter value
err_format_specifier (str) – python format specifier which set the precision of the error
bibliography¶
J.F. Marques, B.M. Varbanov, M.S. Moreira, H. Ali, N. Muthusubramanian, C. Zachariadis, F. Battistel, M. Beekman, N. Haider, W. Vlothuizen, A. Bruno, B.M. Terhal, and L. DiCarlo. Logical-qubit operations in an error-detecting surface code. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.13071, 2021. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.13071.pdf.